Understanding Semantic Caching
In large language models (LLMs), semantic caching entails keeping track of previously calculated answers and the input queries that go with them. Instead of recalculating the output from scratch when a new query is made, the model may rapidly determine whether a similar question already exists in the cache and return a saved response. This is especially helpful for inquiries that request comparable information but may have slightly different language.
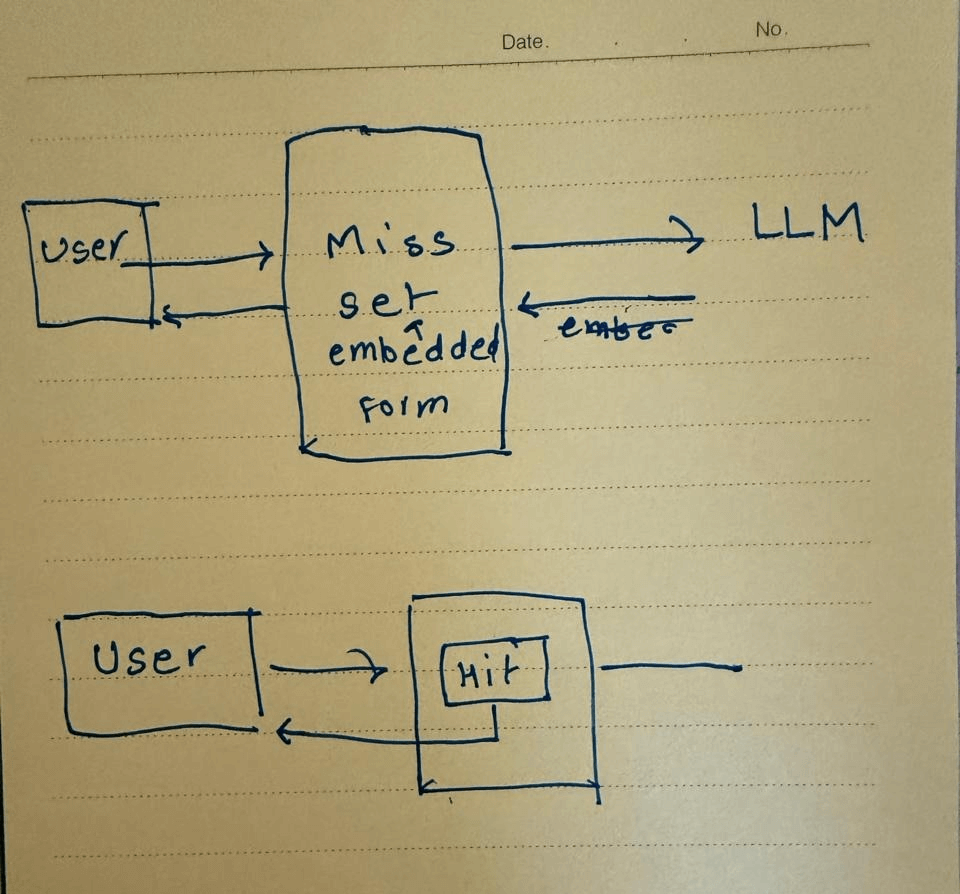
How it works:
The LLM initially looks through the cache for related past queries when a user submits one.
Semantic Matching:
The new query is converted into a vector space using model embeddings (for example, by using BERT or Sentence Transformers approaches). To locate matches, the model compares this vector with cached query vectors.
Response Obtaining:
- Cache Hit: This significantly lowers response time and computational cost by returning the cached response if a match is discovered.
- Cache Miss: The LLM handles the query, produces a response, and then saves the new input-output pair in the cache for later use if there isn't a match.
Conclusion
Large language models can be made more efficient with the innovative method of semantic caching. Allowing these models to employ previously calculated replies will drastically lower latency and computational expenses, which will enhance user experience in a variety of applications.