Databases are among the few constants in computer science that have stood the test of time. However, the way we manage them is evolving rapidly. One modern approach to data management is the serverless architecture for databases.
It enables developers to build applications without needing to worry about directly managing the infrastructure. Let's explore the basics of these serverless database platforms and then setup one using Upstash.
Basics of Serverless data platforms
Let's put it this way, these platforms allow you to use databases without worrying about underlying infrastructure like scaling, hosting, and maintenance.
These platforms typically operate on a pay-per-usage model, which can be beneficial. However, if you get DDoS-attacked, the costs can quickly become a concern. But there are ways around that too. Not the focus of this article.
Here is how it works at a high level:
1. Event-Driven Operations: Serverless platforms operate only when needed avoiding the need of a constantly running infrastructure.
2. Auto-scaling: These platforms usually provide a way to scale automatially. That is the scaling and load balancing of these data platforms are managed by them rather than the developer using these platforms.
I guess that's enough theory. Let's set up a quick Redis Database using Upstash
1. Create your redis database.
Follow this link here. Ideally select the region closest to you.
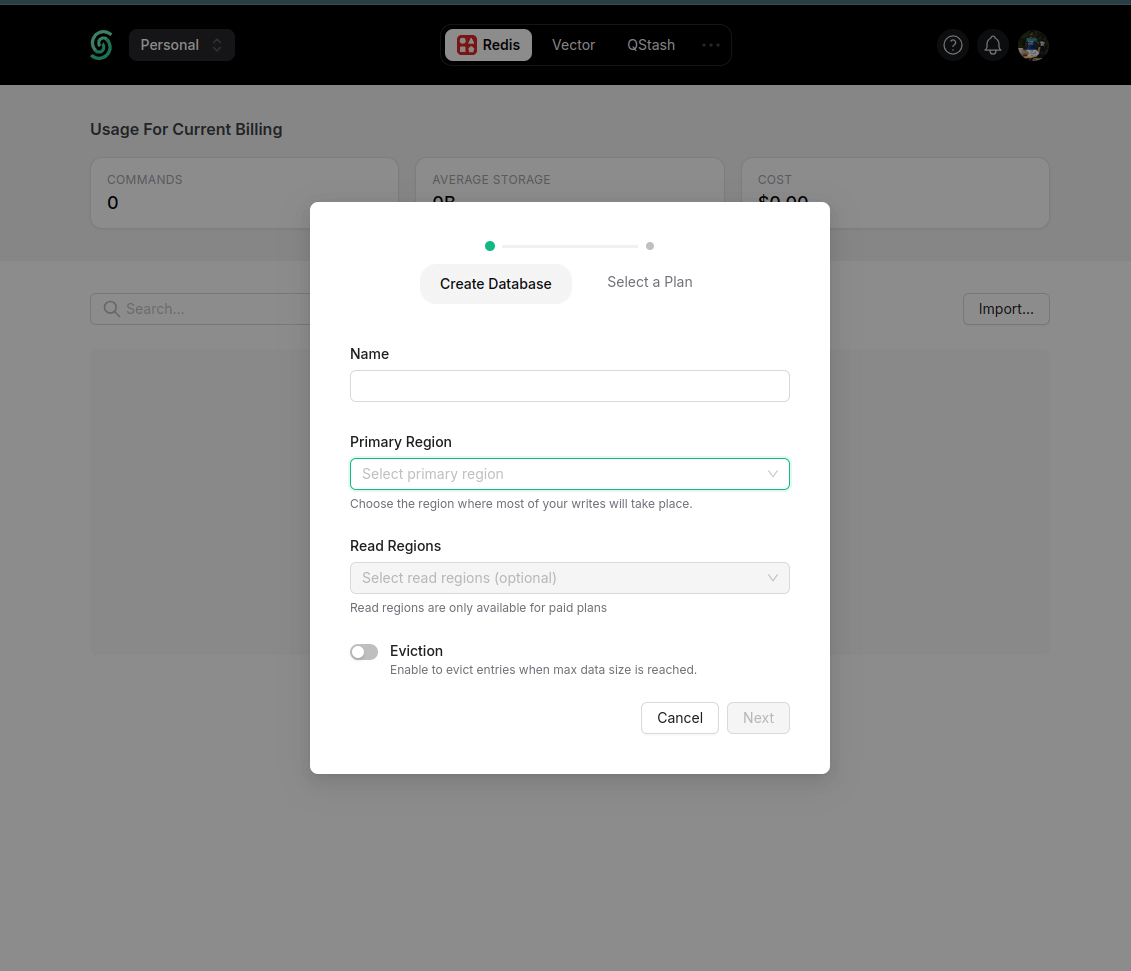
Once the database is created you can get the following secrets on the platform.
UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_URL="https://xyz-1234.upstash.io"
UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_TOKEN="********"Paste these in your project .env file.
Now you can easily initialize this serverless redis database using the following code. Create a file in your libs/utils folder named redis and add the following snippet.
import { Redis } from "@upstash/redis";
const redis = new Redis({
url: process.env.UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_URL,
token: process.env.UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_TOKEN,
});
export default redis;Once you are done with this. Now you can import and use the redis functions in your code.
Something like this:
import redis from "@/lib/redis";
redis.incr('count'); // increments the count by 1
And all set! You can now create and interact with your first Serverless database.